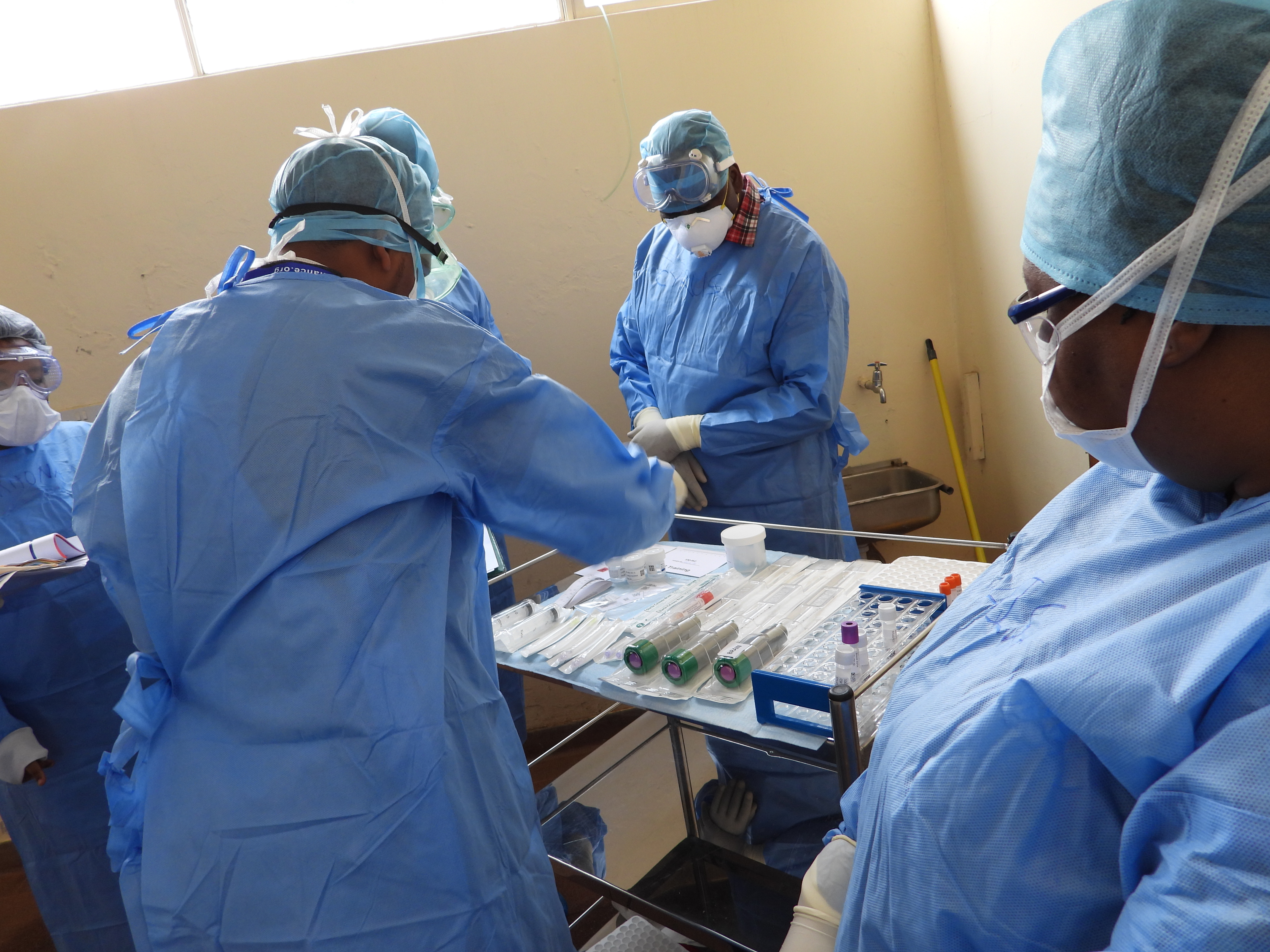
Respiratory infectious disease is common among adults, with estimated annual incidence of 5-20 per cent of all hospital admissions and deaths. However, there are no recent studies describing the causes of these diseases. The proportion of deaths due to COVID-19 is likely to be overestimated in the absence of data on respiratory infectious disease. Complete autopsies are rarely performed for these cases. Postmortem testing of specimens obtained using the Minimally Invasive Tissue Sampling (MITS) techniques are feasible for detection of these infections. This information is essential for the estimation of the respiratory disease burden and for the active surveillance of respiratory infections including COVID 19.
A team led by Dr. Edwin Walong, a lecturer in the School of Medicine, has secured funding from the Minimally Invasive Tissue Sampling Alliance and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation to perform MITS procedures on deceased adults whose clinical causes of death are due to respiratory disease or those who die suddenly of suspected natural causes. The team will test these samples for common viral respiratory diseases including SARS-Cov2, Influenza A, Influenza B, Parainfluenza, Adenovirus, Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Pneumocystis jerovecii and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Other members of the research team include Dr Jared Mecha, Dr Loise Achieng, Dr Dennis Inyangala, Washington Ochieng, Dr Frank Onyambu, and Dr Peter Kibet from the University of Nairobi; Dr. Victor Akelo and Dr. Beth A Tippett Barr from US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Kisumu; Dr Joyce Bwombengi from Mbagathi Hospital, Milka Bunei from Washington State University, Dr Mary Mungania from Kenyatta National Hospital, and Dr Dickens Onyango from the Kisumu County Department of Health.
The research will augment current COVID-19 surveillance initiatives by the Ministry of Health, provide a basis for training in MITS and make available material for additional research into respiratory disease. It will be based at the MITS training hub established in 2019 at the Anatomic Pathology Unit of the Department of Human Pathology (University of Nairobi) and Kenyatta National Hospital. The hub was established through a training grant by the MITS Alliance, a Bill and Melinda Gates funded initiative, to provide global best standards for training and practice of MITS. A trainer of trainer’s course was offered to core MITS training hub faculty by globally acclaimed scientists from the IS Global of the University of Barcelona and the US Centers for Disease Control. The hub has since trained 20 MITS practitioners from Argentina, Ethiopia, Malawi, Rwanda and Tanzania.